Я активно использую
Java Management Extensions (JMX) , особенно в веб-приложениях, чтобы контролировать внутренние компоненты приложения и иногда настраивать некоторые параметры во время выполнения. Есть несколько очень полезных инструментов, поставляемых в составе JDK,
JConsole и
JVisualVM , которые позволяют подключаться к вашему приложению через
JMX и манипулировать открытыми управляемыми компонентами.
Я собираюсь оставить в стороне основные
концепции JMX и сконцентрироваться на интересных случаях использования:
—
показ log4j поверх
JMX (который позволяет изменять LOG LEVEL во время выполнения)
—
показ статистики Hibernate поверх
JMX
Чтобы немного упростить все подпрограммы с помощью представления управляемых bean-компонентов, я буду использовать
Spring Framework, который имеет потрясающую
поддержку JMX, управляемую аннотациями. Давайте создадим наш первый
фрагмент кода Spring :
показ log4j поверх
JMX .
<!--?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?-->
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemalocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!-- Some beans here -->
<!-- JMX related bean definitions -->
<bean id="exporter" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.MBeanExporter">
<property name="assembler" ref="assembler">
<property name="namingStrategy" ref="namingStrategy">
<property name="autodetect" value="true">
</property></property></property></bean>
<bean id="assembler" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.assembler.MetadataMBeanInfoAssembler">
<property name="attributeSource" ref="jmxAttributeSource">
</property></bean>
<bean id="namingStrategy" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.naming.MetadataNamingStrategy">
<property name="attributeSource" ref="jmxAttributeSource">
</property></bean>
<bean id="jmxAttributeSource" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.AnnotationJmxAttributeSource">
</bean>
<!-- Exposing Log4j over JMX -->
<bean name="jmxLog4j" class="org.apache.log4j.jmx.HierarchyDynamicMBean">
</bean>
</beans>
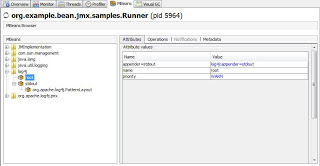
Вот как это выглядит внутри
JVisualVM с установленным плагином VisualVM-MBeans (обратите внимание, что log
LEVEL (приоритет) logger root может быть изменен с WARN на любой, скажем, DEBUG, во время выполнения и сразу же вступит в силу):
Давайте добавим
Hibernate в представление
JMX ! Для этого я создам очень простую
конфигурацию Hibernate с использованием
XML-файла контекста Spring (я повторю настройку для bean-компонентов, связанных с JMX, но она точно такая же, как в предыдущем примере):
<!--?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?-->
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xsi:schemalocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!-- Some beans here -->
<!-- JMX related bean definitions -->
<bean id="exporter" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.MBeanExporter">
<property name="assembler" ref="assembler">
<property name="namingStrategy" ref="namingStrategy">
<property name="autodetect" value="true">
</property></property></property></bean>
<bean id="assembler" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.assembler.MetadataMBeanInfoAssembler">
<property name="attributeSource" ref="jmxAttributeSource">
</property></bean>
<bean id="namingStrategy" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.naming.MetadataNamingStrategy">
<property name="attributeSource" ref="jmxAttributeSource">
</property></bean>
<bean id="jmxAttributeSource" class="org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.AnnotationJmxAttributeSource">
</bean>
<!-- Basic Hibernate configuration -->
<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configurationClass" value="org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource">
</ref></property>
<property name="hibernateProperties">
<props>
<prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.HSQLDialect</prop>
<prop key="hibernate.generate_statistics">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</property></bean>
<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="HSQL"></jdbc:embedded-database>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory">
</property></bean>
<!-- Exposing Hibernate Statistics over JMX -->
<bean name="hibernateStatistics" class="org.hibernate.jmx.StatisticsService">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory">
</property></bean>
</beans>
И теперь мы видим эту картинку (обратите внимание на очень важное
свойство Hibernate , чтобы увидеть некоторые реальные данные здесь
hibernate.generate_statistics = true ):
Круто, просто и очень полезно, не правда ли? ?