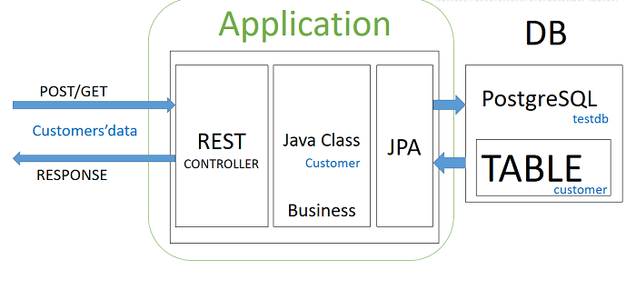
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как использовать встроенный PostgreSQL в вашей локальной среде разработки, а также как использовать его для интеграции / модульного тестирования DAO. Если вы используете и используете PostgreSQL в качестве производственной базы данных, для тестирования DAO должна использоваться та же база данных, что и для производственной базы данных, чтобы обеспечить согласованность поведения и те же предварительные условия среды.
Мы рассмотрим пример приложения Spring Boot:
- Зависимости приложения Spring Boot
- Конфигурация БД со встроенным PostgreSQL для разработки
- Заказчик CRUD разных слоев с данными весны, mapstruct и lombok
- Модульное тестирование DAO со встроенным PostgreSQL с настраиваемым заполнением данных при запуске
Зависимости Spring Boot
Основными зависимостями приложений maven будут типичные зависимости Spring Boot (spring data..ect), а также встроенный PostgreSQL и другие необходимые библиотеки. Я просто выделю встроенный PostgreSQL для БД, mapstruct и lombok для DTO и отображения сущностей и шаблонного кода.
<dependency>
<groupId>ru.yandex.qatools.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql-embedded</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-jdk8</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>Конфигурация БД со встроенным PostgreSQL для разработки
Теперь, чтобы сконфигурировать источник данных для локального указания на встроенный экземпляр среды выполнения PostgreSQL, весенняя конфигурация будет такой:
/**
* the db spring configuration to use in production , to be replaced with actual production configuration , that is for local run only
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class DbConfig {
private static final List<String> DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS = Arrays
.asList("--nosync", "--locale=en_US.UTF-8");
/**
* @param config the PostgresConfig configuration which will be used to get the needed host, port..
* @return the created DB datasource
*/
@Bean
@DependsOn("postgresProcess")
public DataSource dataSource(PostgresConfig config) {
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
ds.setUrl(format("jdbc:postgresql://%s:%s/%s", config.net().host(), config.net().port(), config.storage().dbName()));
ds.setUsername(config.credentials().username());
ds.setPassword(config.credentials().password());
return ds;
}
/**
* @return PostgresConfig that contains embedded db configuration like user name , password
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean
public PostgresConfig postgresConfig() throws IOException {
// make it readable from configuration source file or system , it is hard coded here for explanation purpose only
final PostgresConfig postgresConfig = new PostgresConfig(Version.V9_6_8,
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Net("localhost", Network.getFreeServerPort()),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Storage("test"),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Timeout(),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Credentials("user", "pass")
);
postgresConfig.getAdditionalInitDbParams().addAll(DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS);
return postgresConfig;
}
/**
* @param config the PostgresConfig configuration to use to start Postgres db process
* @return PostgresProcess , the started db process
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod = "stop")
public PostgresProcess postgresProcess(PostgresConfig config) throws IOException {
PostgresStarter<PostgresExecutable, PostgresProcess> runtime = PostgresStarter.getDefaultInstance();
PostgresExecutable exec = runtime.prepare(config);
PostgresProcess process = exec.start();
return process;
}
}Клиент CRUD разных слоев с данными весны, mapstruct и ломбок.
Для образца CUSTOMER CRUD мы будем иметь:
- Клиентский объект
@Entity(name = "customer")
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Customer {
@Id
private long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private boolean isActive;
}- Клиентское хранилище данных Spring
/**
* main customer repository
*/
@Repository
@Transactional
public interface CustomerRepository extends CrudRepository<Customer, Long> {
Optional<Customer> findCustomerByName(String name);
}- Клиент DTO -> Просто DTO ?
- Карта клиента Struct mapper
@Mapper(componentModel = "spring", unmappedTargetPolicy = ReportingPolicy.IGNORE)
public interface CustomerMapper {
CustomerDto mapCustomerToDto(Customer customer);
Customer mapeDtoToCustomer(CustomerDto customerDto);
}Опять же, полный код проекта на Github
Модульное тестирование DAO со встроенным PostgreSQL с настраиваемым заполнением данных при запуске:
- Для конфигурации БД с модульным тестом я намеревался сделать ее немного более подробной, поскольку мне нужно показать, как можно загружать только определенные сущности, DAO и репозиторий данных, поскольку модульное тестирование должно охватывать и ограничиваться только целевым уровнем DAO, а не загружать целые приложения и DAO. Из комментариев и аннотаций вы поймете, как загружать определенные репозитории только с их сущностями.
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackageClasses = {CustomerRepository.class})
@Profile("DaoTest")
public class DbConfig {
private static final List<String> DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS = Arrays
.asList("--nosync", "--locale=en_US.UTF-8");
/**
* @param config the PostgresConfig configuration to use to start Postgres db process
* @return PostgresProcess , the started db process
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean
@DependsOn("postgresProcess")
public DataSource dataSource(PostgresConfig config) {
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
ds.setUrl(format("jdbc:postgresql://%s:%s/%s", config.net().host(), config.net().port(), config.storage().dbName()));
ds.setUsername(config.credentials().username());
ds.setPassword(config.credentials().password());
return ds;
}
/**
* @param dataSource the db data source
* @return the local entity manager factory bean
*/
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean lcemfb = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
lcemfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
// set the packages to scan , it can be useful if you have big project and you just need to local partial entities for testing
lcemfb.setPackagesToScan("io.romeh.postgresembeddeddaotesting.domain", "io.romeh.postgresembeddeddaotesting.dao");
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter va = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
lcemfb.setJpaVendorAdapter(va);
lcemfb.setJpaProperties(getHibernateProperties());
lcemfb.afterPropertiesSet();
return lcemfb;
}
/**
* @param localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean
* @return the JPA transaction manager
*/
@Bean
public JpaTransactionManager transactionManager(LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean) {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean.getObject());
return transactionManager;
}
@Bean
public PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor exceptionTranslation() {
return new PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor();
}
/**
* @return the hibernate properties
*/
private Properties getHibernateProperties() {
Properties ps = new Properties();
ps.put("hibernate.temp.use_jdbc_metadata_defaults", "false");
ps.put("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQL95Dialect");
ps.put("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "update");
ps.put("hibernate.connection.characterEncoding", "UTF-8");
ps.put("hibernate.connection.charSet", "UTF-8");
ps.put(AvailableSettings.FORMAT_SQL, "true");
ps.put(AvailableSettings.SHOW_SQL, "true");
return ps;
}
@Bean
public PostgresConfig postgresConfig() throws IOException {
final PostgresConfig postgresConfig = new PostgresConfig(Version.V9_6_8,
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Net("localhost", Network.getFreeServerPort()),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Storage("test"),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Timeout(),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Credentials("user", "pass")
);
postgresConfig.getAdditionalInitDbParams().addAll(DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS);
return postgresConfig;
}
@Bean(destroyMethod = "stop")
public PostgresProcess postgresProcess(PostgresConfig config) throws IOException {
PostgresStarter<PostgresExecutable, PostgresProcess> runtime = PostgresStarter.getDefaultInstance();
PostgresExecutable exec = runtime.prepare(config);
PostgresProcess process = exec.start();
return process;
}
}- Затем, наконец, класс модульного тестирования:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {DbConfig.class})
@ActiveProfiles("DaoTest")
@Sql(executionPhase = Sql.ExecutionPhase.BEFORE_TEST_METHOD, scripts = "classpath:dao/TestData.sql")
public class PostgresEmbeddedDaoTestingApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
@Test
public void testCustomerSave() {
customerRepository.save(Customer.builder()
.id(new Random().nextLong())
.address("brussels")
.name("TestName")
.build());
Assert.assertTrue(customerRepository.findCustomerByName("TestName") != null);
}
}В нем показано, как загрузить свою тестовую конфигурацию и как вставить некоторые тестовые данные перед запуском тестового примера, используя аннотацию теста JDBC @sql spring.
Надеюсь, это поможет вам понять, как выполнять модульное тестирование DAO с пользовательской загрузкой тестовых данных и использованием встроенного PostgreSQL. Дайте мне знать ваши мысли в комментариях!